
Remember, these examples are intended to provide a better understanding of the concept of incremental cost analysis and its QuickBooks Accountant practical applications. By harnessing the power of incremental cost analysis, businesses and individuals can make more informed decisions and achieve better financial outcomes. Remember, these tips are meant to guide you in effectively calculating incremental costs.

Can incremental cost calculations be utilized for services?
Instead, investors expect a return through potential stock price appreciation and non-guaranteed dividends. In ICSM, system development is divided into a series of incremental cycles, each leading to a decision point, or commitment review. Rather than committing to a full system design early on, stakeholders and engineers make incremental commitments only as far as the evidence and confidence gathered in each cycle justify. This allows projects to pivot, refine goals, or even stop development early https://grvo.app/depreciation-tax-shield-formula-calculator/ if feasibility or value cannot be demonstrated.
- Always consider the relevant factors, time horizon, and assumptions when applying it to real-world scenarios.
- It is usually made up of variable costs, which change in line with the volume of production.
- For example, if the action taken resulted in more revenue, revenues would increase.
- It is often used by the management to evaluate the best possible option or alternatives of investments.
- From a strategic standpoint, decision-makers must evaluate how incremental costs impact the overall cost structure and competitive positioning of the company.
- If four units of product C were removed, the costs for F, V and H would be €72, €80 and €240, equalling €392 in total.
What is the Incremental Cost of Capital?
This guarantees that everything we publish is objective, accurate, and trustworthy. 7 Even the usually cited case of the chairman’s salary has a variable component; if a company reduces in size, one could expect a lower pay for board members. 4 These alternatives will be the subject of a second article, as the prime interest in this article is to consider how to add incrementality into ABC systems rather than to choose between alternative FAC principles. Setting prices in line with a ‘conservative’ LRIC will help to rebut any such challenge.
- This phase involves writing the final code based on the design and development steps.
- When a company’s incremental cost of capital rises, investors take it as a warning that a company has a riskier capital structure.
- For network industries, LRIC estimates could have a crucial role in a price-setting context, supporting regulatory or competition law challenges.
- The annual repairs and maintenance costs for the new machine is 64,000, and the machine will have a 4 year useful life.
- Marginal cost is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in quantity produced.
- In addition to incremental and average costs, many economists today also like to consider the concept of the “actual” cost.
- The incremental cost method recognizes that no additional fixed costs will be incurred if additional units are produced.
How to Properly Record Accrued Revenue for Your Business
As the name suggests, both are meant to calculate the cost and revenue for extra or addition production of goods and services. Thus, the above are some benefits that the procedure of marginal cost analysis contributes to the entire manufacturing process. Like in the above example, it is evident that the per-unit cost of manufacturing the products has decreased from ₹ 20 to ₹ 17.5 after introducing the new product line. Identifying such costs is very important for companies as it helps them decide whether the additional cost is in their best interest. The “incremental” aspect is a key distinction, as the WACC uses the target capital structure for the new project, not the company’s current structure.
Methods to Calculate Production Changes
As these historical costs cannot change, they should not be taken into account when making future decisions, and are not relevant to the incremental analysis approach. The concept of sunk costs describes a cost that’s already been incurred and does not impact any decision made by management or between alternatives. Other terms that refer to sunk costs are sunk capital, embedded cost, or prior year cost. For any business decision that involves changing volumes or adding products/services, incremental costs are vital for determining the financial impact.
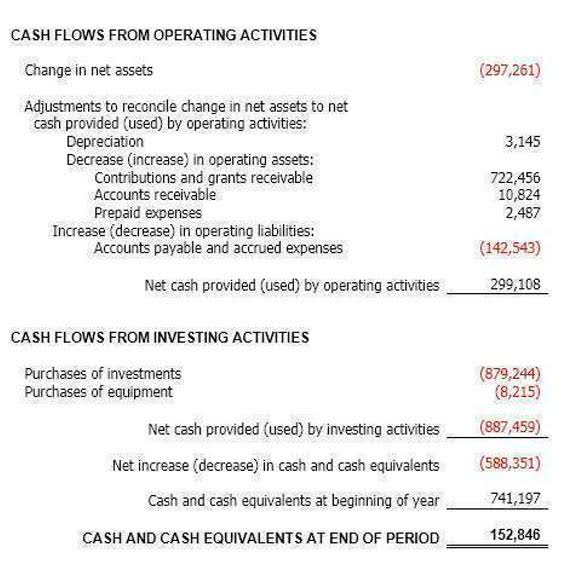

Primary costing models include fully-distributed cost and incremental cost methods. Jamison (2006, 2008) provides a thorough discussion and analysis of these and other costing methods. Assumptions form the foundation of any analysis, and it is crucial to make reasonable and justifiable assumptions. These assumptions provide a framework for our calculations and help us make informed decisions. However, it is essential to recognize that assumptions are simplifications of reality and may introduce uncertainties into our analysis. The relevant costs are those which will change as a result of deciding to outsource the manufacture of the product.
- New preferred stock is a hybrid security that involves issuing new shares that pay a fixed dividend to investors.
- By considering various perspectives and conducting thorough analyses, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their long-term objectives.
- In the box below, a simple worked case is provided showing the calculation of a LRIC for an increment.
- They might evaluate whether the incremental costs of entering a new market are outweighed by the potential revenue gains and strategic positioning.
- In this section, we will delve into the practical application of incremental cost analysis by examining real-world case studies.

In the realm of business and economics, incremental costs play a pivotal role in the decision-making process. These costs, also known as differential or marginal costs, represent the additional expenses incurred when a company decides to increase its level of output or activity. Unlike fixed costs, which remain constant regardless of production levels, incremental costs are variable and fluctuate with the scale of operations. They incremental cost approach are crucial for managers who stand at the crossroads of strategic planning, as they provide a granular view of the financial implications of various choices.

” That’s the question at the heart of incremental cost analysis—a financial tool that separates successful growth from expensive mistakes that the company incurs . All the above processes involve some substantial amount of cost and will also generate much revenue over time if implemented in the correct manner. In most cases, companies utilise incremental analysis to choose between bulk orders and new business opportunities.

